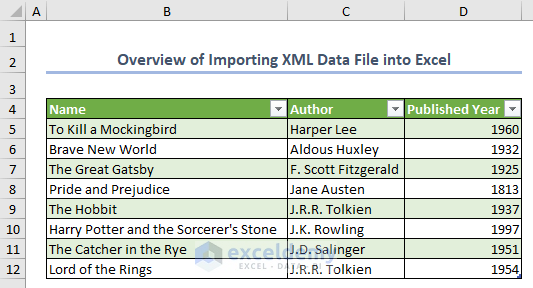

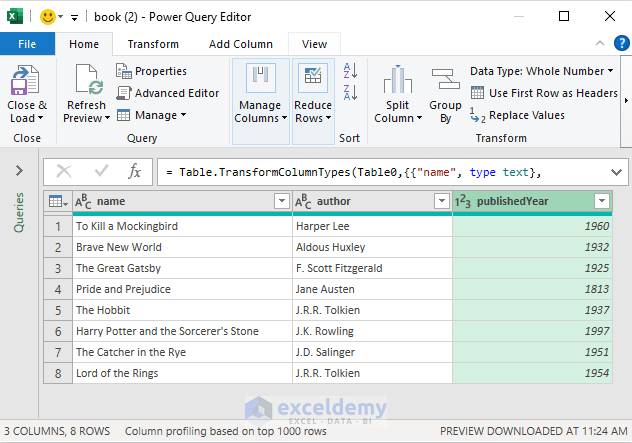
Importing XML data files into Excel allows you to integrate structured data from various sources into your spreadsheets to take advantage of Excel’s research and visual features while dealing with XML-based data. The main advantage to importing XML data is to enable analyzing data from diverse sources in a user-friendly environment. In this article, we will discuss how to import XML data files into Excel in various ways, including using the Data tab, a web URL, the Developer tab with the Source and Import features, and importing multiple XML data files. XML data files will look similar to the image below after importing them into Excel.
An XML (Extensible Markup Language) data file serves as a structured means of storing and organizing data. It’s a plain-text file format that employs a tag-based system, making it both human-readable and machine-readable. XML data files act as a universal language for data exchange that can communicate between different software systems and programming languages.
The data is already stored in XML format.
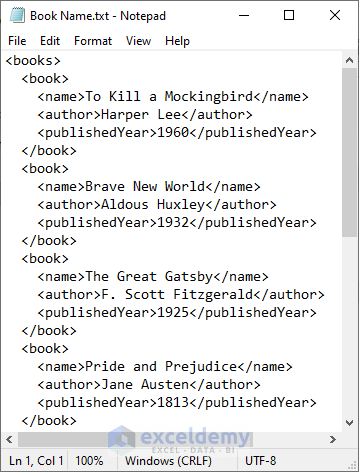
As a result, we now have an XML data file. Let’s import it into our spreadsheet.
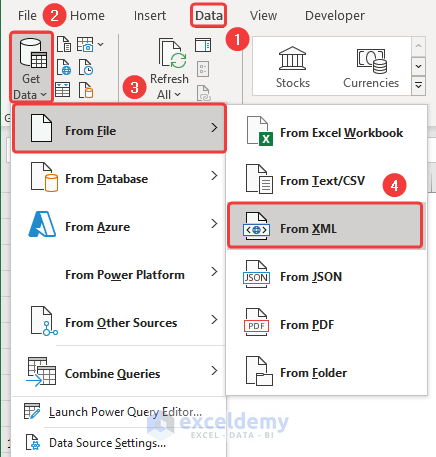
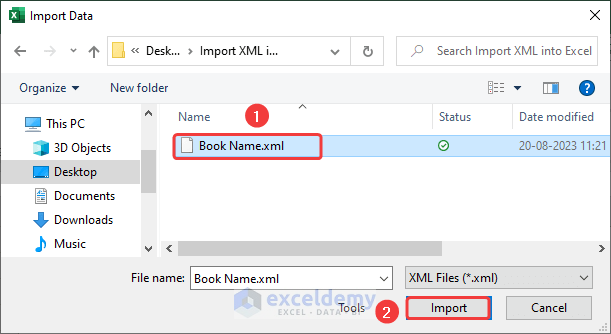
The Power Query window will open.
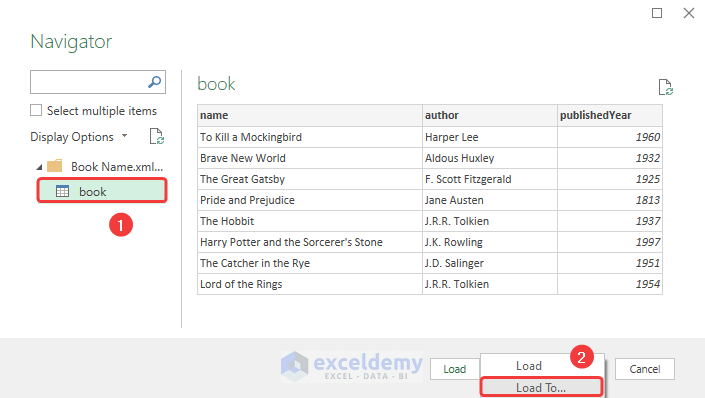
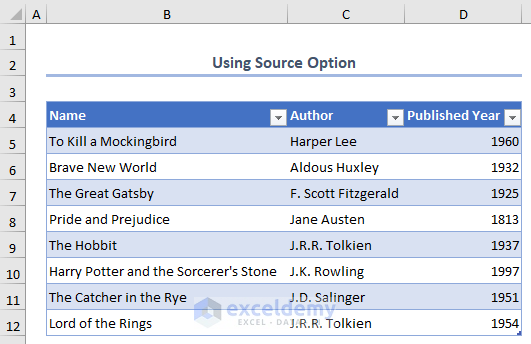
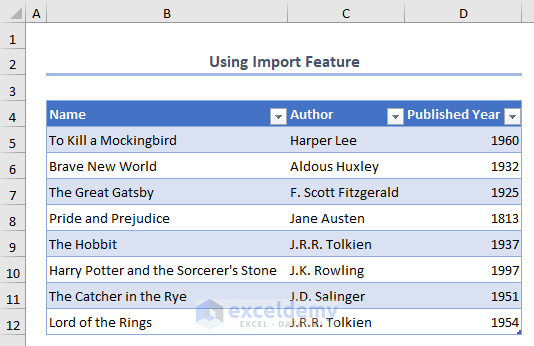
We have successfully imported the XML data file into Excel.
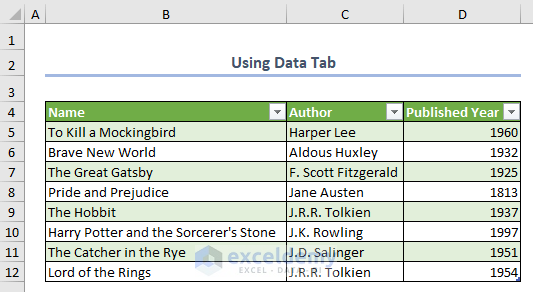
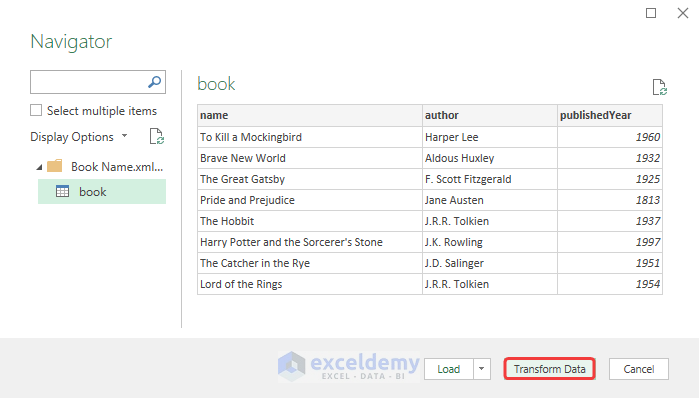
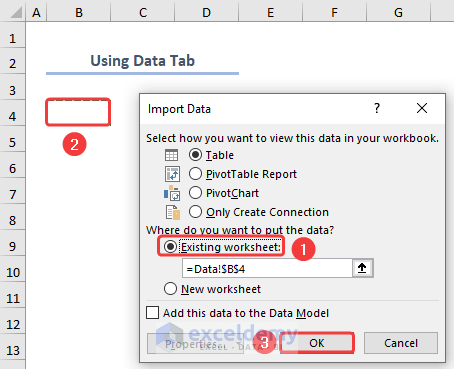
The Power Query Editor will open, where you can edit the data file to make changes to the data table.
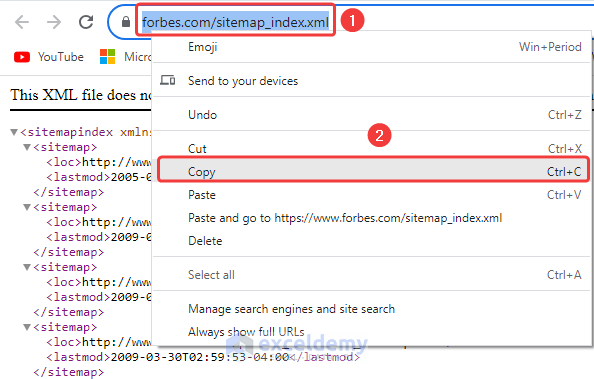
While exploring multiple sites, you won’t be able to download the XML file directly. But you can import XML data using the URL link. Here, we will import XML data from Forbes.
STEPS:
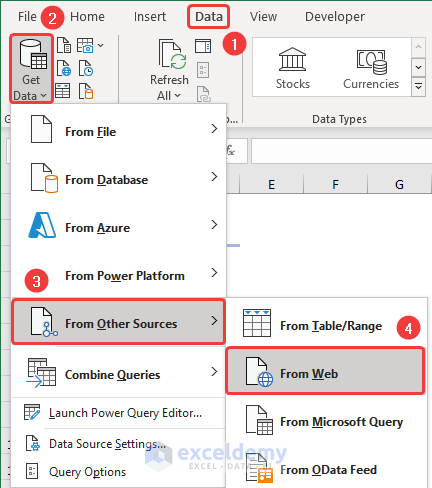
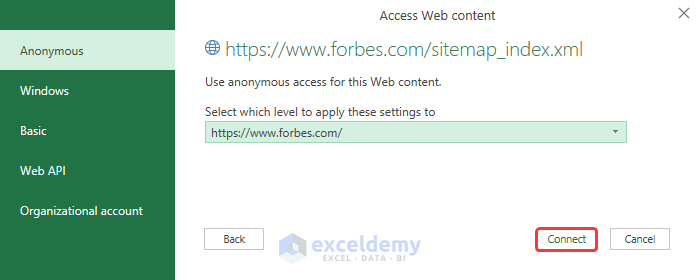
A From Web dialog box opens

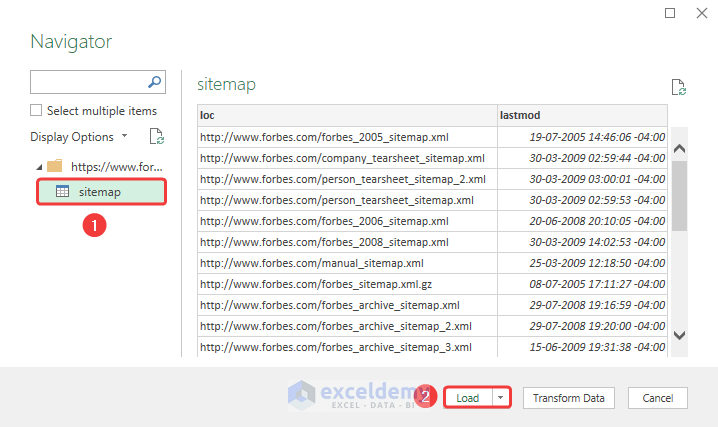
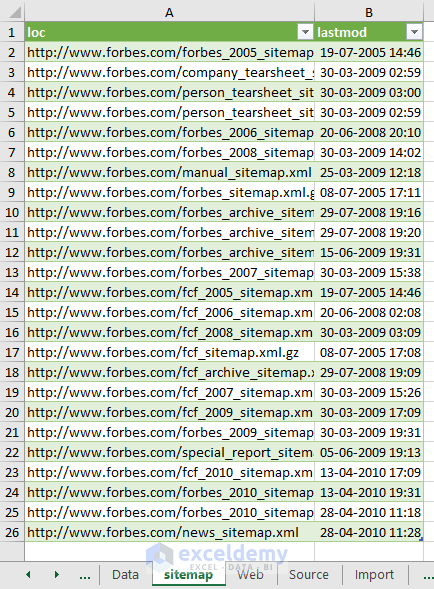
We have successfully imported XML data into our spreadsheet.
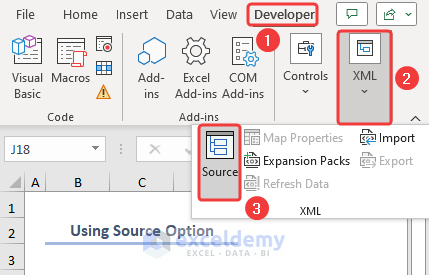
The Developer tab in Excel is primarily used for more advanced tasks related to Excel customization, automation, and macro development. We can use it to import XML data files using 2 different techniques.
 XML Maps window" width="452" height="238" />
XML Maps window" width="452" height="238" />
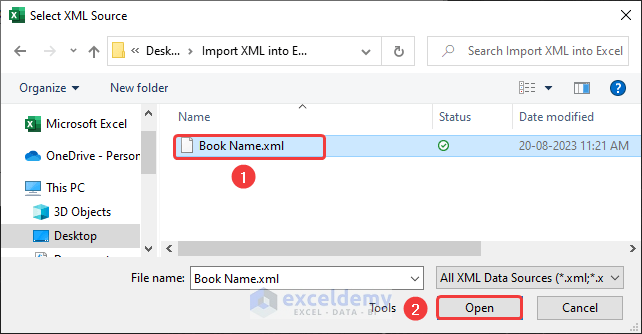
The file is added in the XML Maps.
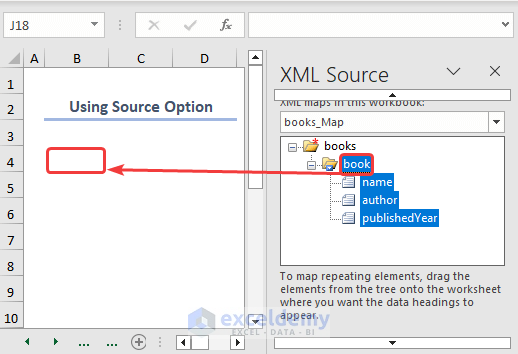
As a result, the table consisting of data will be inserted inside the worksheet.
The XML data file is imported into the spreadsheet.
 Final output with importing XML file inside the spreadsheet" width="531" height="344" />
Final output with importing XML file inside the spreadsheet" width="531" height="344" />
We can import data directly utilizing the Import feature. The XML file will need to be added in the XML Maps window first.
STEPS:
 Selecting the Import feature from the Developer tab" width="404" height="325" />
Selecting the Import feature from the Developer tab" width="404" height="325" />
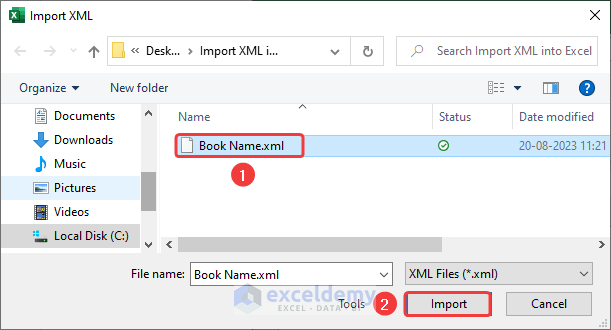
The XML file is imported into Excel.
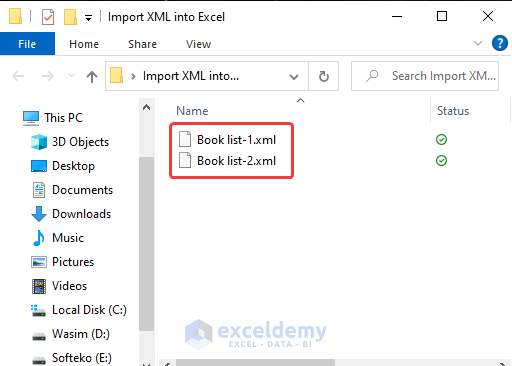
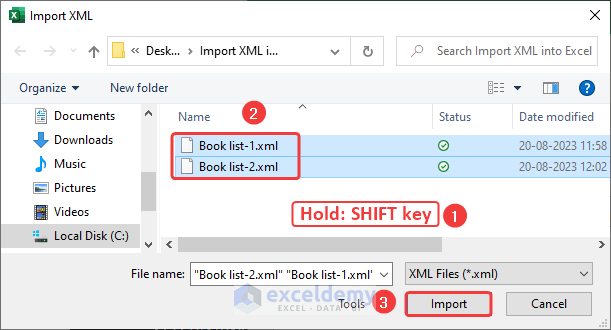
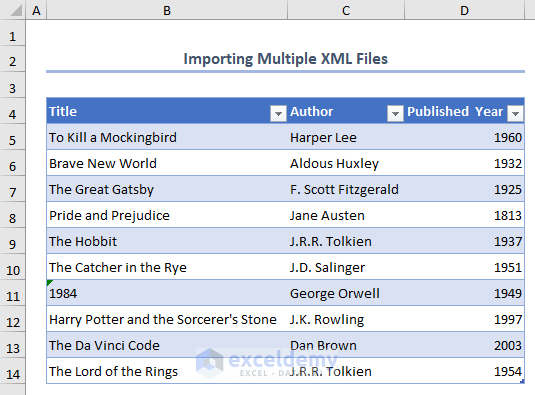
Similarly, we can also import multiple XML files into Excel. Suppose we have 2 XML files containing a Book List in a folder. Let’s import both files into a workbook.
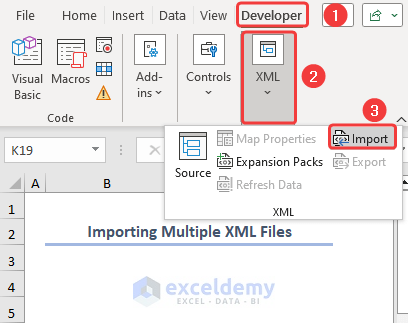
STEPS:
1. Can I customize the import process for XML data?
Yes, you can map XML elements to specific Excel columns, set data types, and configure refresh settings to keep the data up-to-date.
2. What should I do if the XML file has a complex structure or namespaces?
Complex XML structures or namespaces may require more advanced handling. Use Excel’s tools to manage namespaces and map elements to columns manually during the import process.
3. What if there are errors during the XML import process?
If errors occur during import, Excel will provide error messages that describe the issue. You may need to review the XML file’s structure, mapping, or data quality to address these errors.